AgriMamba-Guided Multimodal Framework with Pathology-aware Alignment for Plant Disease Severity Grading
Accurate plant disease grading is essential for effective crop management, yet traditional vision models often fail in complex field environments. To bridge this gap, we present AgriMamba, a novel multimodal framework that leverages pathology-aware alignment for precise severity assessment. Our approach employs a hierarchical three-stage architecture that progressively refines segmentation from the entire leaf to specific fine-grained lesions. The Localization-aware Mamba Leaf Segmenter first efficiently isolates the target leaf and filters out background noise using state space modeling. Subsequently, the Text-guided Mamba Lesion Segmenter incorporates pathological descriptions as semantic anchors to accurately distinguish subtle lesions from natural leaf textures. Finally, the framework quantitatively determines the disease severity grade by calculating the ratio of the segmented lesion area to the leaf. Validated on a comprehensive dataset covering sixteen crop species, AgriMamba significantly outperforms existing methods with a grading accuracy of 97.20%.
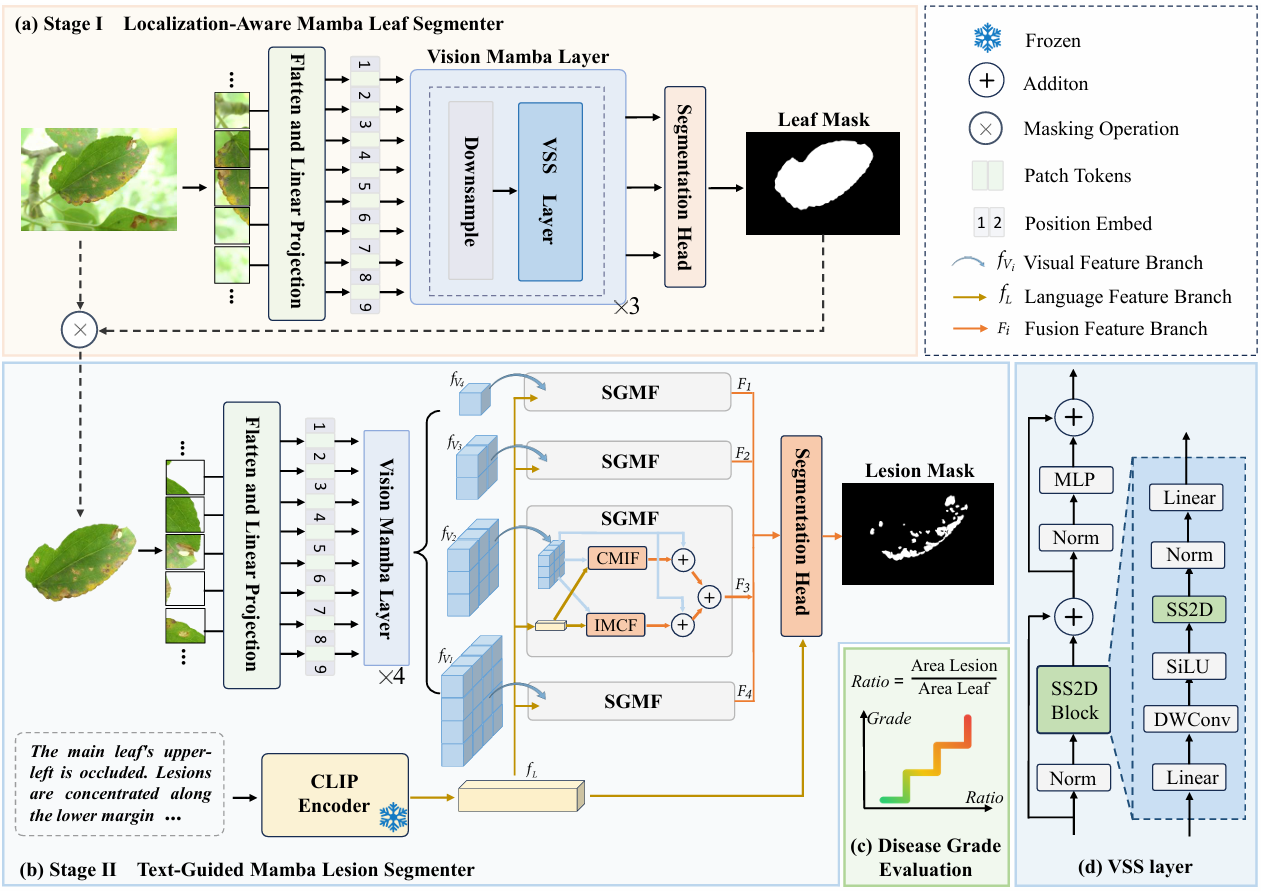
AgriMamba Framework Overview
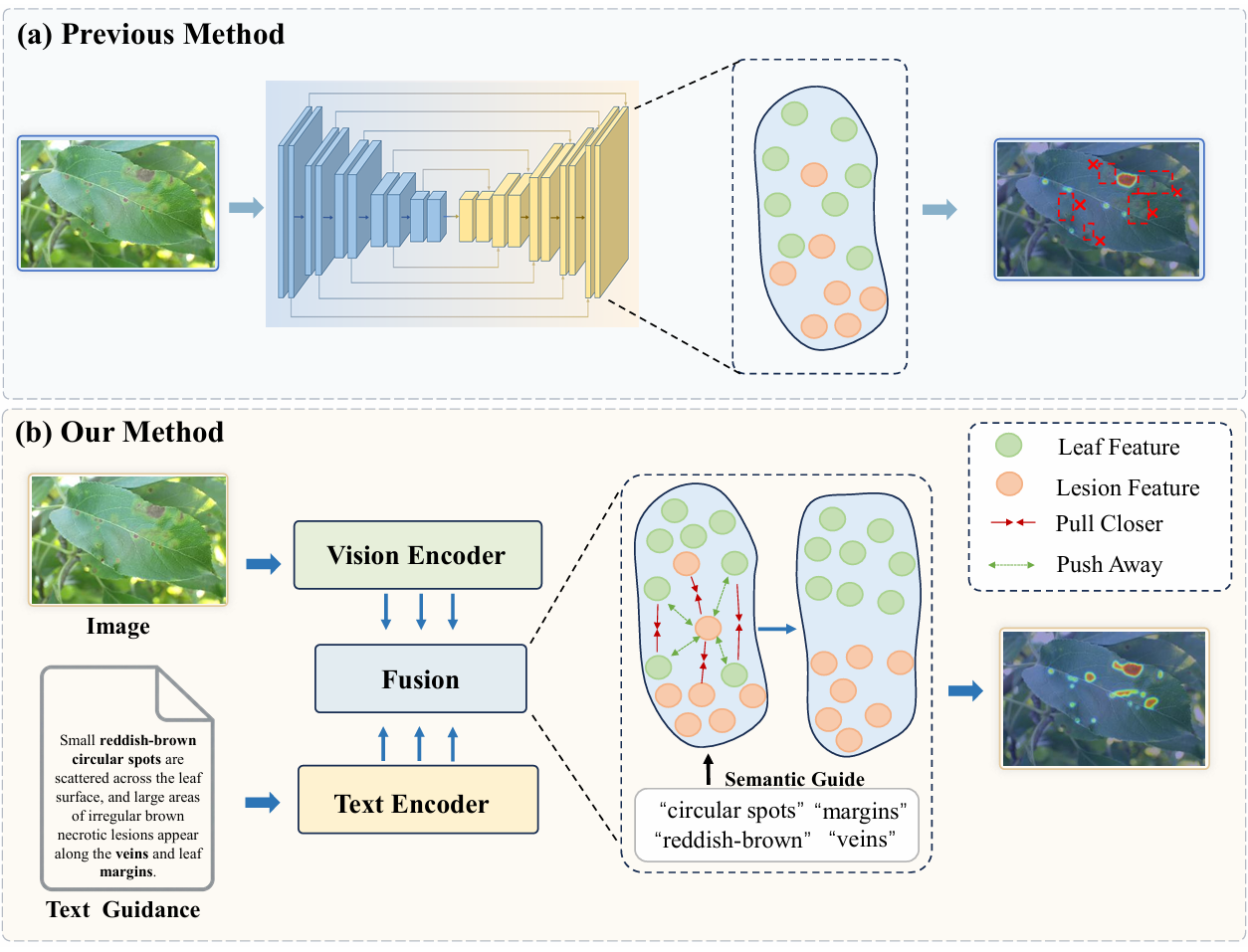
The figure illustrates the overall architecture of the proposed AgriMamba, which consists of three progressive stages for accurate disease grading. In the first stage, the Localization-aware Mamba Leaf Segmenter utilizes the Vision Mamba Layer to extract global features and isolate the target leaf. This module effectively filters out background noise and generates a precise binary mask of the leaf lamina. Subsequently, the Text-Guided Mamba Lesion Segmenter incorporates pathological textual descriptions encoded by a frozen CLIP encoder in the second stage. The proposed SGMF module fuses these semantic cues with visual features to guide the fine-grained segmentation of minute disease lesions. Finally, the framework calculates the ratio of the segmented lesion area to the leaf area in the evaluation stage. This quantitative metric determines the final disease severity grade according to standard agricultural protocols.
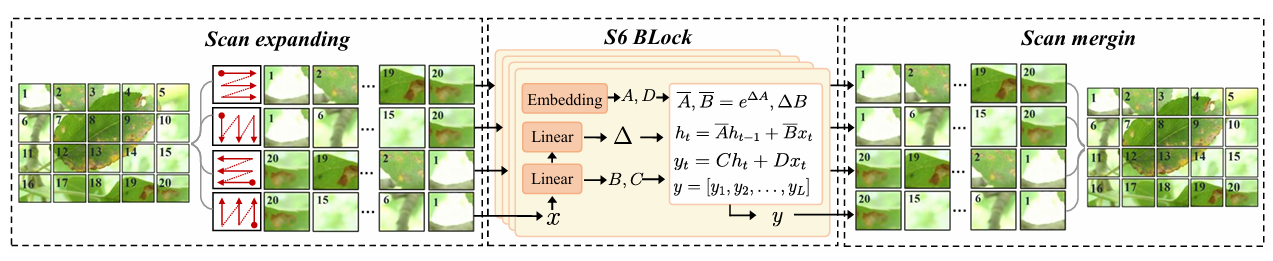
SS2D: 2D Selective Scanning
We employ the 2D Selective Scan (SS2D) mechanism as the primary feature extractor to capture global visual context. Specifically, it flattens the input feature map into 1D sequences along four distinct directions to facilitate cross-directional information flow. Subsequently, the core S6 block processes these sequences with linear complexity and merges them to reconstruct comprehensive 2D features.
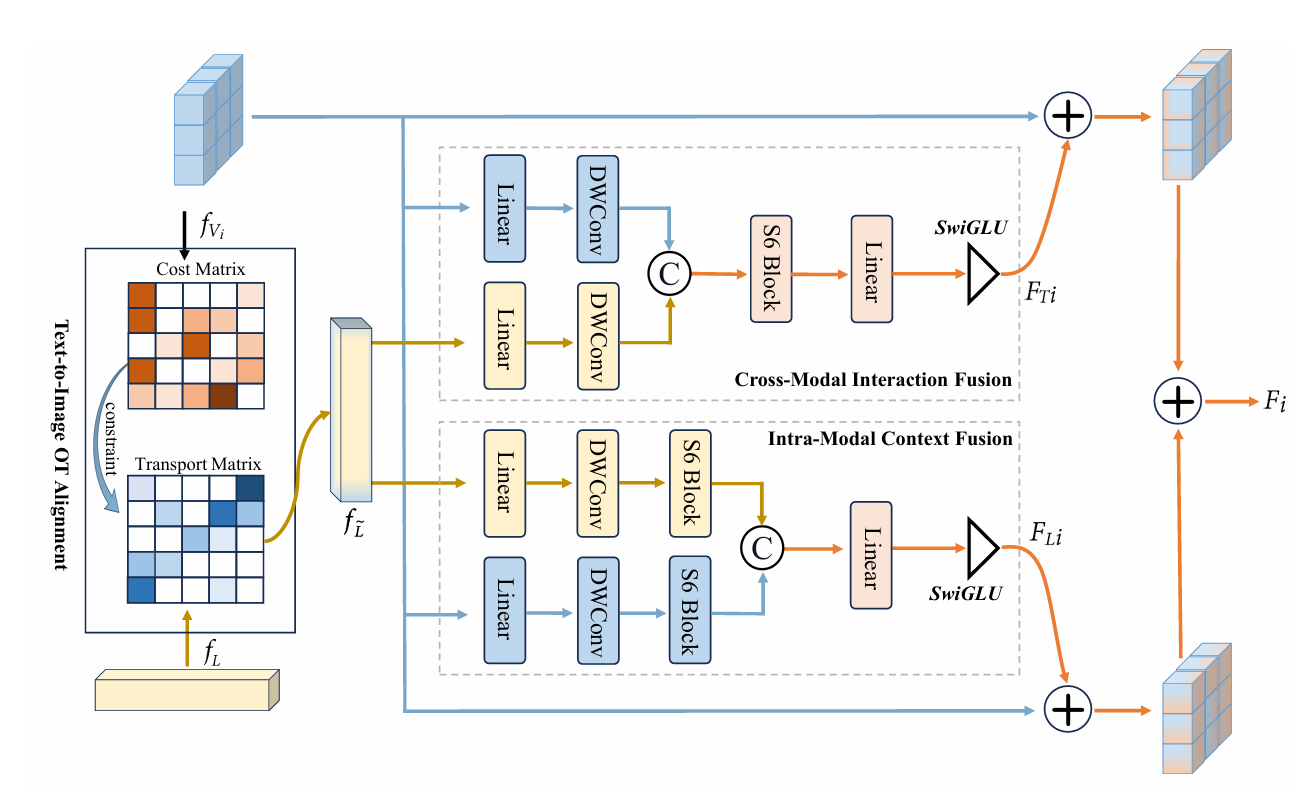
SGMF: Semantic-Guided Mamba Fusion
We propose the Semantic-Guided Mamba Fusion (SGMF) module to effectively bridge the semantic gap between visual and textual modalities. First, the Text-to-Image Alignment unit utilizes Optimal Transport theory to align heterogeneous features and minimize semantic discrepancies. Subsequently, the Cross-Modal Interaction Fusion block deeply integrates visual and textual representations to capture complementary pathological information. Finally, the Intra-Modal Context Fusion component enhances internal feature consistency to ensure the robustness of fine-grained lesion representations.
AgriMamba: Methodology
Introduction
The AgriMamba framework comprises three key components: the Localization-aware Mamba Leaf Segmenter (LMLS), the Text-guided Mamba Lesion Segmenter (TMLS), and the Quantitative Grading Module. LMLS efficiently isolates the target leaf from complex backgrounds using the Vision Mamba architecture. Subsequently, TMLS leverages pathological descriptions as semantic cues to guide the fine-grained segmentation of minute lesions. Finally, the system calculates the disease severity grade based on the area ratio of the segmented lesions to the leaf lamina.
Dependencies
- mamba_ssm==1.1.2
- CUDA 12.2
- Python 3.8
- torch==2.2.1
- torchaudio==2.2.1
- torchvision==0.17.1
- numpy==1.24.4
- Pillow==10.4.0
- einops==0.8.1
- opencv-python==4.11.0.86
Code in github: https://github.com/GZU-SAMLab/AgriMamba
Data
We construct a comprehensive multimodal dataset spanning 16 crop species, including staple crops (Corn, Potato, Soybean, Wheat), economic crops (Coffee, Cotton, Sunflower, Tea), and horticultural crops (Apple, Banana, Citrus, Grape, Lemon, Mango, Peach, Tomato). The dataset contains 10,350 samples, each equipped with pixel-level ground truth masks for both the leaf and lesions, alongside detailed pathological textual descriptions.
Only the test set of the plant leaf disease severity assessment dataset is publicly available for now. The training set will be released once the paper is accepted. You can download the dataset from this link. Download the dataset to the './dataset/' folder.
Get Started
Train Stage I: LMLS
python train_stage1.py \
--output-dir ./output/stage1 \
-epochs 50 \
--batch-size 8 \
--data-set dataset_10350 \
--lr 3e-5
Train Stage II: TMLS
python train_stage2.py \
--stage1-results ./output/stage1/stage1_out_img \
--data-set dataset_10350 \
--output-dir ./output/stage2 \
--epochs 100 \
--batch-size 8 \
--lr 3e-5
Evaluation
python ./ evaluation .py \
--answer ./dataset/dataset_10350/test \
--leaf-checkpoint output/stage1/best_stage1_checkpoint.pth \
--lesion-checkpoint output/stage2/best_stage2_checkpoint.pth \
--output-dir ./output/evaluation \
--batch-size 4 \
--save-intermediate
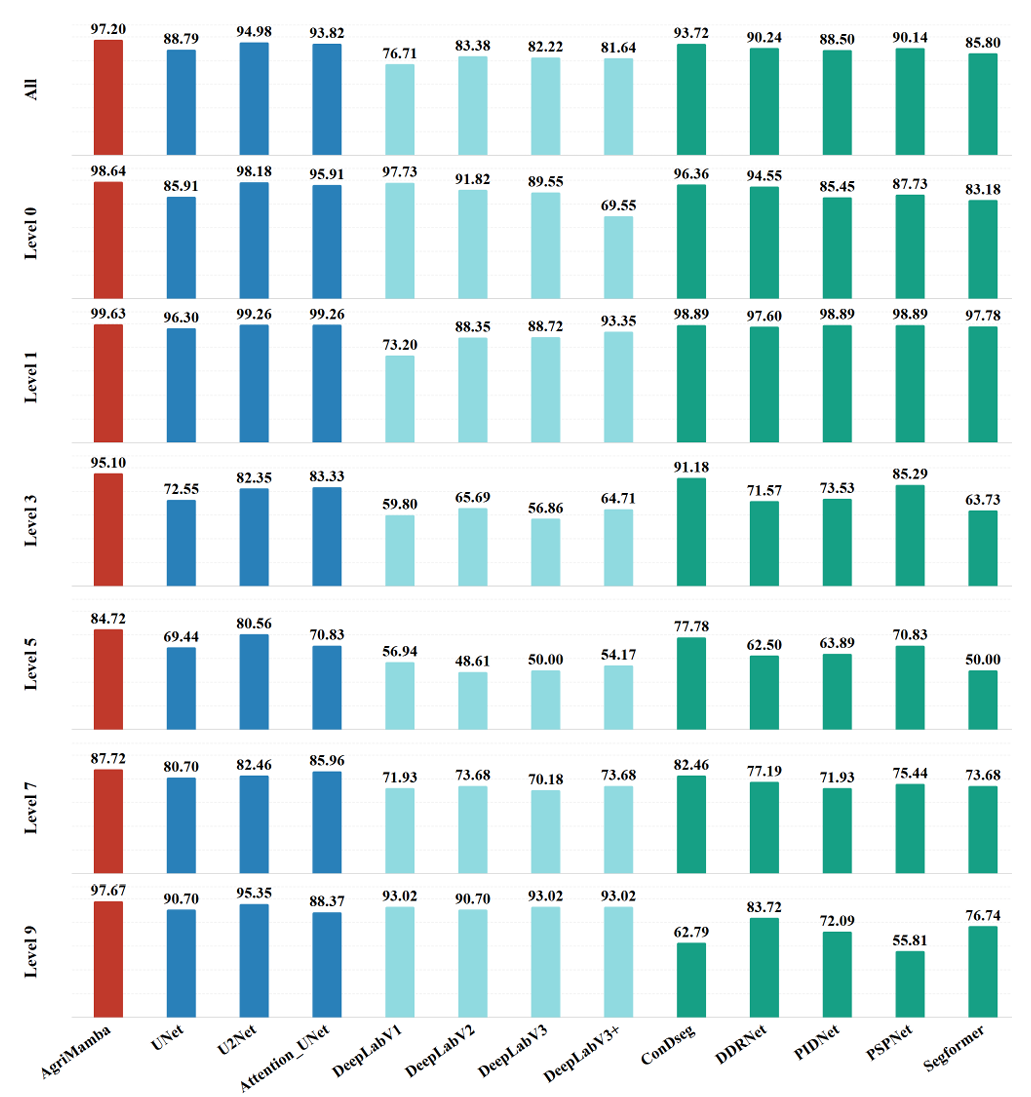
Performance Presentation of Severity Levels
Performance comparison of different models on plant disease severity grading. The bar chart illustrates the Accuracy scores (\%) of the proposed AgriMamba compared to existing methods across distinct severity levels. AgriMamba significantly outperforms all baseline models across all severity levels.
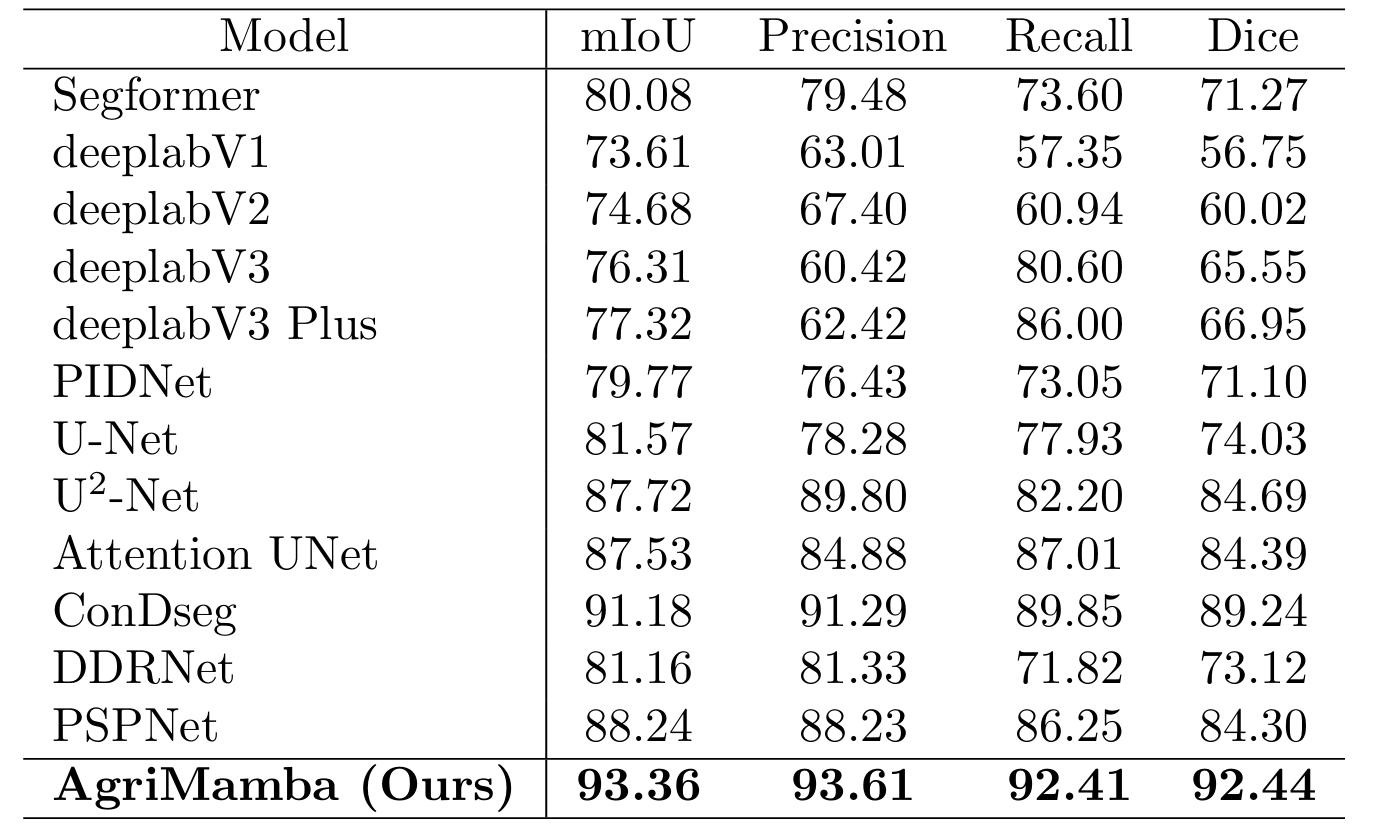
Quantitative Comparisons with Segmentation Models
Quantitative comparison with representative segmentation models on the lesion segmentation. AgriMamba Leads all baseline models across four standard metrics. All evaluation metrics are reported in percentage (\%), and the best results are highlighted in bold.
Qualitative Visualization of Lesion Segmentation Results
Qualitative comparison of plant lesion segmentation results. We compare our method with eight commonly used semantic segmentation networks, and our predictions are the closest to the Ground Truth.

About AgriMamba
Why AgriMamba?
Accurate assessment of plant disease severity is a pivotal component of agricultural management and yield estimation. However, traditional pure vision-based methods often struggle to distinguish subtle pathological features from leaf natural textures. The core reason is that a single modality fails to provide sufficient discriminative information for accurate identification.
Furthermore, recent multimodal approaches utilizing additional information still encounter two critical challenges in complex agricultural scenarios. First, aligning heterogeneous knowledge remains difficult due to the significant semantic gap between visual and textual modalities. Second, existing models struggle to discriminate minute lesions within complex backgrounds, leading to suboptimal segmentation performance. To this end, we propose AgriMamba, which leverages pathological descriptions as semantic anchors to guide visual learning. This approach effectively reinforces visual lesion features and separates pathological patterns from the inherent natural textures of leaves.
To validate our approach, we construct a comprehensive multimodal dataset comprising 10,350 samples across sixteen crop species. This dataset systematically covers Staple Crops, Economic Crops, and Horticultural Crops to ensure broad agricultural applicability. Additionally, each sample is equipped with pixel-level ground truth masks and precise pathological textual descriptions for training.
Research Team
Smart Agriculture and Multimodal Lab (SAMLab)
State Key Laboratory of Public Big Data, Guizhou University
Our research focuses on precision agriculture, multimodal learning, and computer vision applications in plant disease analysis.